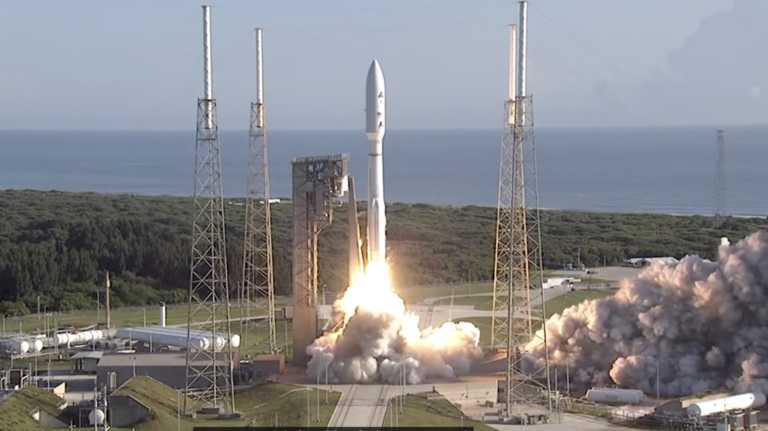
A suggestion made last week by acting #NASA administrator Sean Duffy that SpaceX could be booted from the agency’s upcoming moon-landing plans has rocked the space industry.
Now, behind the scenes, pitches for alternate paths to the lunar surface are quietly starting to take shape.
SpaceX currently has a US$2.9 billion contract to prepare its gargantuan Starship rocket system to ferry astronauts to the moon’s surface as part of NASA’s Artemis III mission. However, citing delays in Starship’s development and competitive pressure from China, NASA asked SpaceX and Blue Origin — which holds a separate lunar lander contract with the space agency — to submit plans to expedite development of their respective spacecraft by October 29. Both companies have responded.
But the space agency is also asking the broader commercial space industry to detail how they might get the job done more quickly, hinting that NASA leadership is prepared to sideline its current partners.
CNN spoke with half a dozen companies about how they plan to respond to NASA’s call to action, which the agency will formally issue once the government shutdown ends, according to a source familiar with the matter.
While some of the potential proposals appear more straightforward than the current moon-landing plan that uses Starship, each involves constructing and testing new spacecraft designs, a process that typically takes at least six or seven years, noted Casey Drier, the chief of space policy at the nonprofit exploration advocacy group Planetary Society.
This could pose an issue for NASA’s timeline. China aims to land its astronauts on the lunar surface by 2030, and Duffy has repeatedly indicated he views beating China as a national security imperative.
Artemis III is currently slated to happen as early as mid-2027, and NASA has signaled that the current pace of Starship development is threatening to push that target months or years into the future.
“There’s a certain part of the moon that everyone knows is the best,” Duffy said, referring to the moon’s largely unexplored south pole region — the target landing site for NASA’s Artemis III astronauts.
“We have ice there. We have sunlight there. We want to get there first and claim that for America,” he said in August.
Experts who spoke with CNN for this article said that reevaluating SpaceX’s lunar lander contract could be wise. Spending years to develop an entirely new spacecraft could still potentially be faster, some argued, than waiting for Starship, which presents extremely difficult engineering challenges due to its sheer size and unprecedented design.
Still, SpaceX has ticked a few boxes that might give it a significant leg up on the competition. Though in light of NASA’s broader lunar ambitions, experts say the real contest is about much more than speed.
More power, more problems
Touted as the most powerful rocket system ever built, Starship has launched on 11 eye-popping suborbital test flights, relighting engines in space, reusing boosters and demonstrating the ability to deploy satellites along the way.
View 352 times
Inside #NASA’s scramble to find a backup moon plan — and the wild ideas companies are pitching

View 308 times
How to spot November’s supermoon, the closest of the year. The moon’s orbit around the Earth isn’t a perfect circle, so it gets nearer and farther as it swings around. A so-called supermoon happens when a full moon is closer to Earth in its orbit. That makes the moon look up to 14 per cent bigger and 30 per cent brighter than the faintest moon of the year, according to NASA.
November’s supermoon is the second of three supermoons this year and also the closest: The moon will come within just under 222,000 miles (357,000 kilometres) of Earth.
Tides may be slightly higher during a supermoon because the moon is closer to Earth, said astronomer Lawrence Wasserman with Lowell Observatory. But the difference isn’t very noticeable.
No special equipment is needed to view the supermoon if clear skies permit. But the change in the moon’s size can be tough to discern with the naked eye.
“The difference is most obvious as a comparison between other images or observations,” said Shannon Schmoll, director of Abrams Planetarium at Michigan State University, in an email.
Supermoons happen a few times a year. One in October made the moon look somewhat larger, and another in December will be the last of the year.
___
Adithi Ramakrishnan, The Associated Press
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.

View 304 times
#NASA takes one step closer to launching quiet supersonic jets. A supersonic jet plane designed to make very little noise took flight for the first time this week, cruising over the southern California desert just after sunrise in what could be the first step toward much faster commercial travel, according to NASA.
NASA and the U.S. weapons and aerospace manufacturer Lockheed Martin successfully tested a jet Tuesday that is capable of travelling faster than the speed of sound.
Aircraft have been capable of flying at supersonic speeds since the 1940s. The problem is that ultra fast planes are banned for commercial travel over land because they make an explosive — and frightening — “sonic boom” that disturbs the public.
The supersonic aircraft Concorde, operated through British Airways and Air France, made transatlantic flights starting in the 1970s. But those were halted in 2003 after a fatal crash three years earlier tanked demand for the expensive service.
If NASA and Lockheed Martin can successfully lower the volume, the new jets could slash travel time between places like New York City and Los Angeles roughly in half, opening up an entirely new air travel industry.
The X-59 is capable of flying faster than the speed of sound with what Lockheed Martin described as only a “gentle thump.” Tuesday’s test flight was still slower than the speed of sound and was intended primarily to test the plane’s structural integrity. Still, it was celebrated as a significant step toward the widespread use of supersonic travel.
The compact, 100 foot (30 metre) plane launched from the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, about 60 miles (100 km) north of Los Angeles, coasted over the desert and landed near NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center about 40 miles (64 km) away.
The first airplane to move faster than the speed of sound — or 767 mph (1,235 kph) — took off nearly 80 years ago in 1947, according to NASA. But flights at that speed were banned over land in the United States soon in response to polling. Residents complained that the noise reverberated through large cities, rattling windows and startling the public.
NASA and Lockheed Martin have for years been working on a solution that would circumvent the noise and lead to regulatory change, in large part to make commercial supersonic travel within the United States possible.
---
Safiyah Riddle, The Associated Press

View 291 times
Inside #Mongolia’s ‘Mars camp’: The extreme adventure that wants to turn tourists into #astronauts.
It’s Day 25. You wake up in your bunk pod in a snow-capped Martian landscape, far from civilization. Outside it’s -30 C (-22 degrees Fahrenheit). After meditating and eating a breakfast of freeze-dried dumplings, you and your six-person crew don space suits over your thermal underwear and head out into the sandstorm on a mission.
This isn’t a fever dream. It’s a month-long survival challenge deep in Mongolia’s Gobi Desert that’s designed to simulate life on Mars — for tourists.
The project, called the MARS-V Project, is under development by MARS-V, a non-governmental organization based in Mongolia’s capital, Ulaanbaatar. They’re working to build a fully-fledged Mars analogue station in the Gobi to prepare for human travel to the red planet — and expect to welcome the first tourists to the mock Mars camp by 2029.
Why Mongolia?
Nowhere on Earth mimics the geography and climate of Mars more closely than Mongolia’s Gobi. An arid, barren landscape with extreme temperature swings from 45 to -40 C (113 to -40 degrees Fahrenheit). The iron oxide-tinted soil has a reddish hue, making it look eerily Martian.
This combination of isolation, altitude and temperature is what makes the site so scientifically valuable as a training ground for scientists and astronauts — and as a test site for equipment and rovers.
For MARS-V, it also offers another potential: tourism.
“Your objective is to survive in an environment that is very, very isolated,’ says Enkhtuvshin Doyodkhuu, MARS-V CEO. “You have to have this simulation mindset that you’re on another planet: you need to feel that if you don’t follow protocol, you die.”
Surviving the simulation
Each participant will have to pass physical, psychological and mental agility tests, then undergo a three-month virtual astronaut training program on everything from oxygen protocol to the psychology of isolation.
Once you arrive in Mongolia, it’s three days of in-person drills in Ulaanbaatar with your new teammates before handing in your phone and beginning the ten-hour journey by bumpy road to the site, drifting away from civilization across stretches of pale-red dust.
“It’s surreal,” says Doyodkhuu. “This feeling of vastness, of endless empty space — the Gobi really gives you that “Mad Max” kind of feeling. It’s beautiful if you think about it, but it can be overwhelming to some.”
Your home for the month? Mars “habitats” — interconnected modular pods with living quarters, a laboratory and a greenhouse. Each day begins with the same strict daily regimen that real astronauts might face: vitamins, meditation, exercise, breakfast and a team briefing for the day ahead.
“Meditation has to be a big part of the program,” says Doyodkhuu. “One very risky thing when it comes to Mars pioneers is we don’t really know what’s going to happen with their psychology, because no other person has been away from Earth that long.”
Doyodkhuu says the Mars simulation for tourists could have a similar psychological effect.
“You’ll have this sort of claustrophobia; you’ll miss your Earth.”
Days at the MARS-V camp are filled with challenges and tasks: for example, the crew might take the rover out to conduct geological mapping or collect soil samples. Communication with “Earth” (the MARS-V mission support team) happens on a timed delay to mimic interplanetary lag. Simulations take place between October and March in brutal winter conditions, when the Gobi freezes solid.
“Minus 27 C (-16.6 degrees Fahrenheit) would be a warm day,” laughs the CEO. Crews wear thermal base layers, overalls, and analog spacesuits when working outdoors.
To make it as realistic as possible, the team from MARS-V will hide all external support out of sight.
“Compared to an Arctic expedition, this is controlled,” Doyodkhuu says. “If there was any real chance of death, we’d stop the simulation.”
Meals will feature freeze-dried Mongolian dishes — like rehydrated dumplings or mutton stews — designed to mimic astronaut rations while honoring local culture.
There’s even a design echo between the nomadic Mongolian ger — the traditional felt tent sometimes referred to as yurts — and the Martian dome prototypes being developed by the MARS-V engineering team.
“We [Mongolians] have thousands of years of history living in isolated places, with very limited resources,” Doyodkhuu explains. “We’re just taking that idea to another planet.”
Part of history
The idea of trialing planetary life on Earth isn’t new. NASA and ESA have long used analog sites for experiments and training.
But MARS-V’s plan to merge scientific research with tourism arrives at a pivotal moment: private space travel is finally edging into the mainstream. SpaceX and Blue Origin are drawing celebrities like Katy Perry, Tom Hanks and Kim Kardashian into a new era of luxury space tourism.
But, for those who can’t afford a US$28 million ticket to space, Mongolia’s MARS-V camp will offer a more accessible way to experience that cosmic allure at a fraction of the cost, expected to be around $6,000 per person for a month at the camp, and pre-camp training and evaluation.
It’s Mars tourism, without the launch cost — or the suffocating risk of decompression.
MARS-V’s analog station is in the early stages of development, with designs for the habitat, space suits and food completed. Doyodkhuu says they expect the habitats to be ready and open to the public within the next two to three years.
For those drawn to the idea of other planets, MARS-V promises a glimpse of a Martian future.
“You have a lot of time to think out there,” says Doyodkhuu. “Being in this otherworldly place for one month trying to survive with five other people, it gives you this renewed outlook on life.”
“If you believe that humans will become a multiplanetary species in the future, actually being part of this history, going to an analog astronaut training center and challenging yourself, is going to leave a big impact on people.”
For the right traveller — whether thrill-seeker, explorer or space enthusiast — it may be the ultimate holiday. But if the thought of freezing cold isolation and bunk pods sounds more like punishment than adventure, Mongolia’s Gobi already offers glimpses of the otherworldly in a far more comfortable setting.
During the summer at the Gobi’s luxury Three Camel Lodge, travellers can switch thermals for a spa towel and freeze-dried stews for an extensive whiskey selection. You will still need to strap in for the journey though, it takes 7 to 8 hours to reach the lodge from Ulaanbaatar. This is after all one of the most remote places on Earth - and perhaps the closest you can get to Mars, without leaving the planet.
By Rosanna Philpott, CNN

View 315 times
Tropical Storm Lorenzo forms in the Atlantic Ocean, MIAMI — Tropical Storm Lorenzo formed Monday in the central tropical Atlantic Ocean and isn’t threatening land, forecasters said.
The storm was located about 1,095 miles (1,762 kilometres) west of the Cape Verde Islands and had maximum sustained winds of 45 m.p.h (72 km/h), the U.S. National Hurricane Center in Miami said. It was moving northwest at 17 m.p.h (27 km/h).
No coastal watches or warnings were in effect.
The storm was expected to turn northward on Tuesday, with some gradual intensification possible by midweek, forecasters said. The forecast track through Saturday shows Lorenzo staying out in the ocean and away from land.
The Associated Press

View 369 times
Planet announces new line of satellites for daily Earth imaging

View 369 times
#WASHINGTON — A group of former senior U.S. defense officials is urging the #Pentagon to dramatically expand investment in advanced hypersonic weapons and manufacturing capacity, warning that #China and #Russia are outpacing the United States in developing high-speed, maneuverable missiles that threaten to erode U.S. military deterrence.

View 370 times
SYDNEY — An Australian company that is a leader in taking images of spacecraft in low Earth orbit is seeking to widen its aperture to monitor higher orbits, and even beyond.
During an event on the sidelines of the International Astronautical Congress here, Will Crowe, co-founder and chief executive of HEO, highlighted the progress the company has made in what is formally known as non-Earth imaging, or using spacecraft to image other spacecraft in orbit.
HEO does not operate its own satellites but instead works with several Earth imaging companies, partnering with them to access those satellites when they are not being used, such as when passing over oceans. “Pairing our mission with theirs is a really fantastic collaboration,” he said. “It allows us to bring the lowest cost to our partners.”
HEO has conducted 4,000 “missions,” which is what the company calls a flyby by an imaging satellite with a target of interest. Those missions have imaged more than 800 spacecraft, ranging from Starlink and Project Kuiper satellites to the Chinese space station Tiangong.
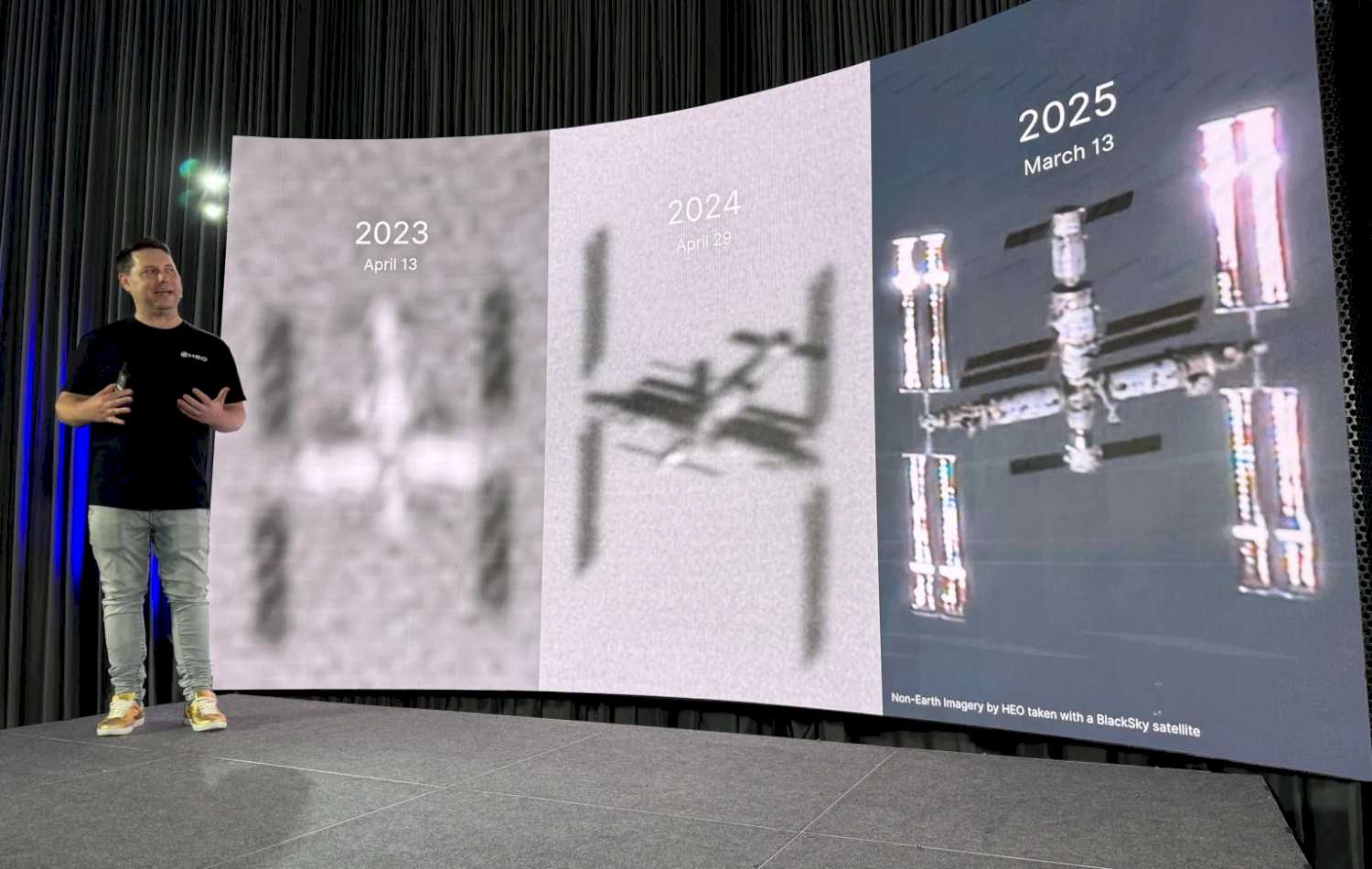
Advances in imaging technologies and techniques, including cameras HEO developed, have resulted in dramatic improvements in quality. Crowe showed a series of images of Tiangong starting in 2023, when the company’s images showed only basic details of the station: a 5 on the company’s 1-to-10 scale of image quality, he said.
He contrasted that with one taken earlier this year that was far sharper, a “10+” quality image that had enough resolution to make out details on individual modules and the articulation of the station’s robotic arm. “You can almost make out the writing on the side,” he said.
The imagery has helped satellite operators diagnose problem with their spacecraft. “Now we can inspect satellites in space,” Crowe said. “When you satellite fails, there is a way to see how it has failed.”
In one case, HEO imagery showed a satellite was tumbling, allowing the operator to detumble and recover the spacecraft, while in another, imagery showed a solar panel had not deployed. “We’ve already helped a bunch of companies correct their satellites and get their missions back on track.”
The company has been able to observe satellites at altitude of up to about 700 kilometers, but Crowe said HEO is working to install cameras on other satellites to enable observations of satellites at up to 1,200 kilometers. “This is where a lot of critical assets are, and there’s a lot of tensions about the things being launched those altitudes,” he said.
HEO plans to aim much higher, though. Crowe announced at the event that the company is working to install cameras on spacecraft to enable observations in the geostationary belt. “All our customers have been asking us to get to GEO for a long time,” he said.
HEO plans to work with unnamed partners on spacecraft in “monitoring orbits” a few hundred kilometers above and below GEO. That will include the capability to maneuver to inspect individual spacecraft if needed.
The company plans to being service in January 2027. “We’ve already had customers who have bought into this,” he said.
“HEO’s mission is to image anything in the solar system on demand,” Crowe said, and that goes beyond spacecraft in Earth orbit. The company is studying ways to use spacecraft in GEO to image asteroids that make close approaches to Earth.
“Just last year, there were four asteroids that passed close enough that a satellite in GEO or near GEO with a camera could potentially use a little bit of fuel that it would need to use anyway to get to a graveyard orbit but instead pass by an asteroid that happened to be floating past,” he said.
Such imagery could be used for scientific purposes or even resource extraction, he said. HEO estimates that at least 30 asteroids more than 19 meters across will pass “really close” to the GEO belt and be potential targets for imaging missions. The best-known example Apophis, a large near Earth asteroid that will pass inside the GEO belt in April 2029.
“This is an opportunity that is too good to miss,” he said. “We’re going to go past this asteroid in 2029, which we’re incredibly excited about, all using a GEO satellite at the end of its life.”
View 352 times
L3Harris looks to scale production of hybrid satcom radios after successful Air Force tests.
WASHINGTON — L3Harris Technologies said it has successfully demonstrated a satellite-based radio system that allows military aircraft to tap commercial space broadband services such as SpaceX’s Starlink while maintaining encrypted, government-grade communications.

View 404 times





Space news on Umojja.com